 In the developed countries infectious diseases are no longer the major causes of death. The average life expectancy is now about 76 years. As people age however they become prone to disease of the heart and blood vessels, and cancers, and these two types of disease account for about two thirds of all deaths in developed countries.
In the developed countries infectious diseases are no longer the major causes of death. The average life expectancy is now about 76 years. As people age however they become prone to disease of the heart and blood vessels, and cancers, and these two types of disease account for about two thirds of all deaths in developed countries.Cardiovascular disease in Britain’s biggest killer, accounting for about 40% of all premature deaths. The two major cardiovascular diseases are coronary heart disease, which accounted for about 25% of all deaths in Britain in 1990 and strokes, responsible for about 10% of all death in Britain in 1990. Overall this is between 300 to 400 people per day and represents about a five fold increase since the Second World War. It is not surprising then than cardiovascular disease has been called the “modern epidemic” as it is on a scale comparable to major infectious diseases of the past. Unfortunately Britain has one of the highest rates of cardiovascular disease in the world and in 1992 the Government set targets aimed at reducing its incidence. The targets acknowledge the fact that to alarge extent the deaths are avoidable and that it is important to understand their causes and to try to develop more effective strategies to reduce the numbers of deaths.
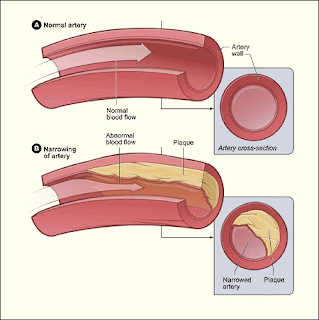 Atherosclerosis
AtherosclerosisBy far the most common cause of cardiovascular disease is atherosclerosis. The process leading to atherosclerosis stats with the deposition of yellow fatty streaks containing a high proportion of cholesterol in the inner coat of arteries. The deposits form beneath the inner are deposited in the cholesterols and these often start to calcify and become hard, a process known as arteriosclerosis. The deposits are referred to as athermanous plaques. As a plaque increases in size it protrudes into the occurs in the aorta and coronary arteries which supply the muscles of the heart. If the plaque breaks through the smooth endothelium, its rough surface commonly cause a blood clot to develop. This is called a thrombus which may build up until it is large enough to block the artery. If clot breaks away, it may block an artery at another location. A clot that breaks away like this is called and embolus.
The artery wall is made weaker by athermanous plaques and may stretch as a result. Local stretching is called aneurysm. It may rupture, a process known as hemorrhage. This is more likely if arteriosclerosis have occurred. Once an artery is blocked the tissue it supplies will suffer oxygen starvation and will be severely damaged or die. If thrombosis occurs in a coronary artery the heart is damaged and a heart attack any occurs. This medical term for heart attack is myocardial infarction. (
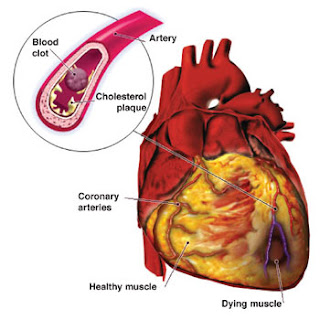 Myocardial refers to heart muscles; infraction means suffocation due to lack of oxygen.) If thrombosis occurs in the brain (cerebral thrombosis) a stroke may occurs. Strokes are sometimes referred to as cerebra vascular accidents. They are also caused by cerebral hemorrhage. They usually result in permanent damage to the cerebral hemispheres due to oxygen starvation. The cerebral hemispheres are the conscious part of the brain and control may functions such as speech and motor coordination. Both heart attacks and strokes may result in death.
Myocardial refers to heart muscles; infraction means suffocation due to lack of oxygen.) If thrombosis occurs in the brain (cerebral thrombosis) a stroke may occurs. Strokes are sometimes referred to as cerebra vascular accidents. They are also caused by cerebral hemorrhage. They usually result in permanent damage to the cerebral hemispheres due to oxygen starvation. The cerebral hemispheres are the conscious part of the brain and control may functions such as speech and motor coordination. Both heart attacks and strokes may result in death.A muscle that is excercised without an adequate blood supply will give rise to pain as a result of cramp. When the heart is involved, such as pain is called angina. An angina attack may be brought on even by gentle execise such as climbing stairs. The pain may spread out from the center of the chest to the neck, jaws, arms and back.
 Thus coronary heart disease has two main forms, angina and mycocardial infraction (heart attack). A heart attack may be caused by a coronary thrombosis or simply by narrowing of the artery by atherosclerosis until the blood supply by narrowing of the artery by atherosclerosis until the blood supply is sufficiently restricted. About half a million people a year in Britain have heart attacks and about one third die as a result. Half of these die within one hour. There are now great efforts taken to try to avoid these deaths by carrying special equipment in ambulances and by suitable treatment in hospital casualty units. Drugs can be used to restore normal heart rhythms and a heart which has stopped beating can sometimes be restarted by administration of an electrical shock across the chest wall.
Thus coronary heart disease has two main forms, angina and mycocardial infraction (heart attack). A heart attack may be caused by a coronary thrombosis or simply by narrowing of the artery by atherosclerosis until the blood supply by narrowing of the artery by atherosclerosis until the blood supply is sufficiently restricted. About half a million people a year in Britain have heart attacks and about one third die as a result. Half of these die within one hour. There are now great efforts taken to try to avoid these deaths by carrying special equipment in ambulances and by suitable treatment in hospital casualty units. Drugs can be used to restore normal heart rhythms and a heart which has stopped beating can sometimes be restarted by administration of an electrical shock across the chest wall.






Comments (0)
Post a Comment